Research Methodology – A Comprehensive Guide

Quick Navigation
For students, who have embarked on formal research for the very first time, can be quite overwhelming. They might get intimidated by all the technical lingo that surrounds research like research methodology, analysis, methods etc. There are so many things to focus on and staying on top of everything may seem difficult. For the novice and aspiring researchers, the task to take on formal research is a mammoth task as they have to formulate a research proposal, decide on the research methodologies and explain their decisions concerning several aspects of the research. We have put together this article in an easy-to-digest format and it is dedicated to research methodology so that novice researchers can grasp a clear understanding of the structure of research methodology and put together an effective research methodology in their research paper. After going through this article you will be able to say with satisfaction “it immensely helped me in my paper writing“.
What does Research Methodology mean?
To understand what research methodology implies, let us first understand what a research paper is. A research paper is a type of academic writing where researchers take up a systematic investigation about a certain topic, explore all the related information they can find to come up with certain discoveries or outcomes, interpret such outcomes, conduct analysis, specify limitations of the study and summarize everything with appropriate thematic statement into a coherent narrative. Research methodology is a crucial part of the research. It refers to the system of methods that analyzes the principles and procedures of the study followed in a particular discipline. Students of university and higher education levels are assigned to write research papers, so PenMyPaper recommends you learn how to write a research paper.
A research methodology is a guide as to how the researcher designs a systematic plan to address the research problems and research objectives, and ensure the viability and reliability of the research. It is about how you plan to put your study into practice and explain why you think this is the most effective way to approach your research. In writing a dissertation or thesis, you have to provide a rationale for your study. Research methodology encompasses the following questions that you have to provide answers to in the methodology section:
- What approach you have followed?
- What are the research methods you have employed?
- Why have you chosen such techniques and methods?
- What are the data collection methods?
- What methods have you used to analyze the data?
As per PenMyPaper, you must prepare a research paper outline that will enable you to incorporate key points so that you have a sketchy outline of what your paper will look like.
Significance of Research Methodology
It is with the help of a research methodology that you provide a rationale for your study and give justification for the approach you have taken for your research. You may consider it as a blueprint or an outline that you follow to conduct your research practically. It is through a research methodology that you explain how your plan of action will turn into a valid study that will produce reliable and authentic results. All of these are done considering the objectives of your research.
It is important to correlate your chosen methods to your research hypothesis or questions when you are writing your research methodology. Preparing a hypothesis is important in research paper writing so it’s better if you learn how to write a hypothesis. You must clearly describe your research methods and include sufficient details so that other researchers can replicate the study or implement it in a similar research framework.
One can easily deviate from their track and divert from standard methodology while carrying out research. Devising a research methodology prevents you from getting diverted and keeps you on track with your objectives and provides you with a viable plan to keep your research more manageable, effortless and effective.
It’s better to go through some research paper example to gain knowledge on how to write a paper on it.
Note: Sources and references that back up the choice of research techniques should be included in the research methodology in comparison to the literature review which gives a basic framework and outlook for your research.
How to Frame a Research Methodology?
By far you must have understood the approaches to take for your research methodology. Let us now discuss the structure of a research methodology and how to write it. In general, a research methodology is devised by following a specific model. This makes the process easier to understand for the readers. One of the most popular models followed by the researchers to prepare and construct their methodology is the Research Onion Model.
Research Onion Model- Concept
When writing a research methodology, researchers need to make several decisions and these decisions are illustrated in the Saunders’ Research Onion Model. It is a framework, with the help of which a robust methodology for research can be devised. The objective of this model is to enable students to develop a research methodology in a well-organized manner and explain the several stages of writing the methodology. It facilitates systematic research and helps researchers make a set of decisions with respect to the research. It is an effective tool for thinking about the methodology holistically.
Why Is Research Onion Popular in Writing A Research Methodology?
Every research aims to produce valid and credible findings and to ensure that, researchers have to provide logical reasoning and explanations for each stage of decisions taken towards the methodological approach. The Research Onion framework is most commonly used for preparing a research methodology because it is easier to follow as it provides a pictorial explanation of the several aspects of the study to be analyzed. It can be followed for conducting any type of research. It allows students to plan their methodology in an orderly manner and put together a feasible research design. It provides a guideline that the researchers follow through all the stages that they take when devising a research methodology.
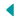
Research Onion Model
Try peeling an onion from the inside out. You can’t do that as you have to begin peeling it from the outside. This is exactly how the Research Onion model works.
For designing a feasible research methodology, researchers begin with formulating research question(s), planning objectives which are followed by a sequence of decisions in regards to the selection of research philosophy, research approach, research strategies, methodological choices, time horizons, to finally data collection and analysis.
These six layers of research onion are correlated and co-dependent. To put it simply, the choice of research philosophy impacts the approach, which in turn affects the decision of methodological choice, research strategy, time horizon, and finally data collection and analysis.
The Research Onion framework has 6 main layers that are described as follows:
Research Philosophy
It is a set of principles relating to the worldview or nature of the reality from which the research is being carried out. It determines how a particular set of data is gathered, inferred and used in research. It is generally studied in terms of epistemology and ontology. Commonly used research philosophies are positivism, interpretivism, realism and pragmatism. Whatever philosophy you choose should correlate with the aims and objectives of your study and should be correctly justified.
- Ontology: It focuses on how we view the world
- Epistemology: It focuses on how we should examine the world.
Positivism Philosophy
Positivist research is based on the concept that knowledge subsists beyond what is being examined. That is to say, whatever is being assessed can only be done with objectivity. It is free from personal opinions and beliefs- the researcher only observes and does not construe. According to positivists, knowledge can either be true or false or meaningless. Positivism asserts there can only be one reality and that all senses remain the same throughout all subjects.
As per the positivist, knowledge can only be attained from empirical study. As the empirical study is based on measurement and observation, knowledge is thus considered a posteriori knowledge- which implies that it does not depend on human reasoning but is obtained from research.
Interpretivism Philosophy
Interpretivism stresses on the impact that cultural and social variables can have on a person. This theory necessitates the researchers to play an active role in the research because it is important to draw a holistic view of the participants’ behavior, meanings and thoughts. In the light of the socio-cultural context, this theory focuses on the views and opinions of people.
Realism Philosophy
Realism is based on the idea that the world exists independent of human mind. Realism describes the nature of reality. Realism, as a division of epistemology, relies on the supposition of a scientific approach to the knowledge development. It claims that any phenomenon or social objects, external to or regardless of individual mind, influence the way individuals perceive the world. Realism philosophy can be of two types- direct and critical realism. Direct realism claims that our senses perceive the world correctly- what we see is what we perceive. Whereas, as per the critical realism, whatever we experience are just sensations, it differentiates between the real and perceivable world- the real world can’t be observed and the perceivable world is what we know and is built from our experiences.
Research Approach
In a typical research methodology, inductive and deductive approaches are most commonly used. A research approach refers to the broader process or plan that comprehensively discusses the methods of data collection, data analysis and data interpretation.
The inductive approach: It is often called a “bottom-up” approach that starts with observations, then examines patterns, and tentatively formulates a hypothesis to produce a new theory. The techniques include generating theories from the research. This approach is applied when you have to answer as to why something happens- as there is a lack of theory to explain the event.
The deductive approach: It is also called a “top-down” approach, begins with a theory to test a hypothesis and then collects the observations that ultimately lead to confirmation of whether or not the data collected and analyzed aligns with the theories. This approach is applied when the research question is to explain what is happening.
Research approaches are based on the nature of the study and the research problem to be answered.
Methodological Choices
Three different choices in research methodology are- quantitative, qualitative and mixed-method. This layer helps to determine whether you should use one methodology or combine qualitative and quantitative methodology.
Quantitative Method
Quantitative research methodology is generally used more for measuring and examining numerical data. The researchers who adopt a scientific paradigm usually follow this approach. When your research objective is to confirm something, you can use this methodology.
For instance, if your research objective is to determine the relationship between two variables or assess a set of hypotheses, you can implement a quantitative methodology.
Qualitative Method
If your research needs to collect and analyze textual data or words, then you can adopt a qualitative research approach. Typically, qualitative methodology is used where the research aims and objectives are explorative. Your aim may be to understand human nature or actions, which are based on qualities and can’t be measured in numerical terms. So, you can use this approach where you are examining something that has an attribute or a characteristic property and that cannot be expressed in numbers.
For example, you are studying human nature which could be for a study in psychology or sociology field. Similarly, you may want to understand the perception of people on a candidate running for president, then you can use this method for your study.
Mixed-Method
It is a contemporary method of research that is a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. You can derive some definitive numbers and facts with the help of a quantitative approach, on the other hand, your research will gain an interesting concept through a qualitative approach.
Research, where you can employ a mixed-method approach, will give you some interesting facts and results. Since a mixed methodology utilizes both quantitative and qualitative approaches, the data and results it produces are both confirmatory and explorative.
Research Strategies
Research strategies refer to the overall procedure by which the research is to be conducted. It is important to provide a rationale as to why and how the procedures and techniques you have employed in the data collection and analysis are best suited for your research. Experiments, case studies, surveys, grounded theory, ethnography etc., are some of the most common research strategies. The strategy to be employed depends on the nature of the study that is whether the study is confirmatory or exploratory.
Survey
Surveys are the most commonly used and economic strategy. It is most effective in generating quantitative data which can be examined empirically. This research strategy is predominantly used to verify causal variables between various types of data. It is very useful method to produce reliable, credible and large quantity of data. Surveys are mostly used in quantitative research. It involves sampling a particular demography or representative percentage of the population. It helps observing contributing variables among different sets of data. This strategy is usually associated with the deductive approach.
Experimental Research
When researchers have to test relations between two variables, they use experimental strategy to alter or modify a variable that is independent to determine a change in the other variable that is dependent. Experimental research aims at proving or disproving or validating a hypothesis.
Experimental strategy adheres to the principles of the scientific method. It is carried out in a controlled environment like a laboratory. The experimental research strategy generally deductive as it tries to examine prevailing theories instead of developing new theories.
Archival Research
As the name implies, this strategy involves the extraction of information from original archives. The archive is a depository that contains historical records and non-current documents. The archival research strategy makes use of existing primary resources and materials to establish a meaning with the help of an examination of that information. It is suitable especially for historical research as it makes use of sources like manuscripts, documents and records.
Case Studies
A case study is a detailed analysis of a person or a group, an event, a problem etc., from a social or psychological or medical point of view. In a corporation, a case study is a careful study of some social unit that aims to identify the factors that led to its failure or success. Case studies are employed to analyze a subject and obtain an in-depth understanding of the context of the study. It does not necessarily infer the findings.
Case studies tend to take an inductive approach and are qualitative in nature. It is important to include the socio-cultural background when taking up case studies. Moreover, since the researcher’s understanding and assumptions are important in case studies, and interpretivism philosophy is usually adopted.
Time Horizon
This is to give the exact timeline in which all the work related to the research has been carried out. Typically, there are 2 types of time horizons namely, longitudinal and cross-sectional.
A cross-sectional time horizon: It refers to the collection of data at a particular point in time. In this time horizon, the duration of time in collecting the data and the process of examination is confined to a short period. It is used for a study that is concerned with the examination of a certain phenomenon at a particular time.
A longitudinal time horizon: It involves collecting data and analyzing them over an extended period. This implies, that the researcher examines events and behaviors for a longer period with the help of concentrated samples. It is used when you have to establish causal relationships, discover relationships, and conduct studies that are observational.
Data Collection and Analysis
Finally, we reach the core of the onion. This is where you make decisions regarding research procedures and techniques. Data collection and analysis strategies depend on the nature of the study- quantitative or qualitative, overall aims and objectives, limitations, and practicalities of the research.
In this section you have to specify the following:
- What data you will collect and all the tools and methods you will use to collect the data.
- What will be the sampling methods (snowball sampling, convenience sampling, systematic sampling etc.)?
- What type of analysis you will employ to address the research questions?
- A summary of the study area and the reason for selecting the locale.
Data Collection
For quantitative research, the following tools can be utilized to collect data:
- Surveys (physical and online)
- Experiments
- Case studies
- Existing data
- Questionnaires
For qualitative research, the following methods can be utilized to collect data:
- Focus groups and group interviews
- Interviews (can be structured, unstructured, semi-structured)
- Documents and records
- Observations and case studies
Data Analysis
In quantitative research, the data analysis approaches include:
- Descriptive statistics (medians, means, modes)
- Statistics for making inferences (regression, correlation etc.)
In qualitative research, the data analysis approaches include:
- Content Analysis
- Analysis of Narratives
- Thematic Analysis
- Grounded theory
- Examination of Discourse
- Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis
Data coding is the first step in qualitative data analysis, followed by one or more techniques of analysis.
Summing up
Preparing a research methodology can be arduous, especially for students who are undertaking research for the first time. You may even require a research paper introduction example at an initial stage. You have to keep in mind your research problem and the aims and objectives of your study. These will help you decide the appropriate methodology and help put together the whole research and writing in a coherent whole. And if you are still struggling with it, then don’t worry, we have got you covered. Just say write essay for me and you can get the entire paper written by academic professionals of PenMyPaper.